ASHE Journal
@ASHE_JournalAntimicrobial Stewardship and Healthcare Epidemiology, open access journal of @SHEA_Epi, published by @CambridgeUP Email: [email protected]
Similar User

@OFIDJournal

@CIDJournal

@IDWeekmtg

@JIDJournal

@MAD_ID_ASP

@SHEA_Epi

@ICHEJournal

@TransplantIDNet

@IdBowl

@AST_IDCOP

@StanfordASP

@SIDPharm

@accpinfdprn

@gonzalobearman

@Women_in_ID
Bringing up some scary bugs this Halloween: Description outbreak CPE in large regional public hospital intensive-care department amongst patients with severe COVID-19 infection requiring intubation and broad-spectrum antimicrobials bit.ly/4hsrEBx
Another trick or treat! A quasi-experimental analysis comparing antimicrobial usage on COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 wards bit.ly/40y3IXo
Trick or treat: From @CDC_NCEZID: The number of outpatient antibiotic prescriptions in the U.S. declined during the COVID-19 pandemic; however, prescribing volume exceeded baseline levels from Oct-Dec, 2022. bit.ly/48sII6u
From @HFrostLab: Outpatient Automated Stewardship Information System (OASIS©), a free, open-source tool for automating clinician feedback reports, presents an effective approach to antimicrobial stewardship. bit.ly/48oiQIQ
SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity among healthcare professionals in a rural state #covid19 bit.ly/4fkIVL7
From @pakpourlab: The spatial and temporal effect of electrochromic windows on indoor and human microbiome in an inpatient hospital bit.ly/48oqKSy

The effect of carbapenem-resistant versus carbapenem-susceptible Enterobacterales infections on patient outcomes at an academic medical center bit.ly/4hgGqvr
Appropriateness of Empiric Initiation of Meropenem in the Intensive Care Unit as Determined by Internal Medicine Residents bit.ly/3YHooeo

A high prevalence of antibiotic use at two large teaching hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a point prevalence survey bit.ly/3zZgfsl

@WashUID: Across two years of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, in HCP without history of #COVID19, anti-N seropositivity rate was associated with exposures SARS-CoV-2 exposures and COVID-19 symptoms. bit.ly/3Aho4cM
Receipt of Phenotype-Desirable Antimicrobial Therapy (PDAT) was associated with hospital characteristics and pathogen characteristics and less with patient characteristics bit.ly/3NAUhiw
Hope you all enjoyed #IDWeek2024…the editorial team (some of whom pictured here) are eager to receive your manuscripts of projects and ideas from the meeting!
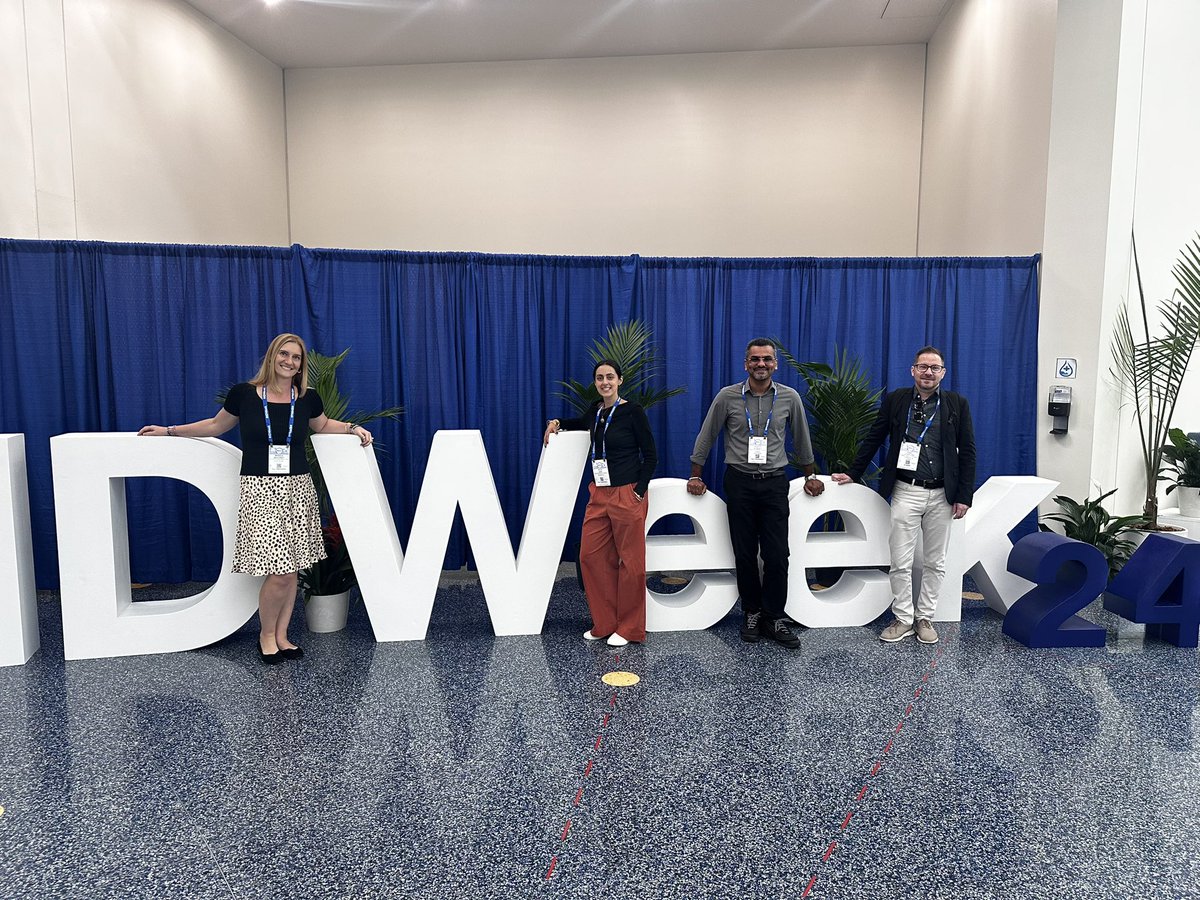

We are always grateful to ALL of our reviewers, but particularly grateful for our top reviewer!

Hope you all enjoyed meeting the editors!


Meet the Editors at the BugHub Stage! 📝✨ Join us today at 8:30 a.m. for a Q&A session with editors from @CIDJournal, @OFIDJournal, @jpidsociety, @ASHE_Journal, and @ICHEJournal . Get insider tips on publishing and industry trends! #IDWeek2024

Pediatric COVID-19 hospitalizations in Canada increased upon emergence of the Omicron variant, and pre-existing health conditions were common; however, disease severity remained low (>90% survival). bit.ly/3UfcTYV
Inappropriate RX’s for a popular topical corticosteroid-antifungal combination product may be common. Learn more from this ASHE Concise Communication! bit.ly/4dP4x1d
New in Careers! Dr. SB Wey: a path of influence and discovery in hospital epidemiology bit.ly/3Ud3i4N
Reducing central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI) by improved identification of primary infection sites through preliminary blood culture notifications bit.ly/48cWUAD
From @VCUHealth (@gonzalobearman et al): In this RCT evaluating 7,625 gloves used by members of distinct surgical services, intra-operative glove failures varied by glove brand, and were frequently undetected by the glove wearer. bit.ly/3Yv9s37
United States Trends
- 1. Chiefs 111 B posts
- 2. Josh Allen 40,7 B posts
- 3. 49ers 36 B posts
- 4. Geno 32 B posts
- 5. Niners 6.889 posts
- 6. Mahomes 31,5 B posts
- 7. Bo Nix 13,8 B posts
- 8. #KCvsBUF 18,3 B posts
- 9. Super Bowl 16,1 B posts
- 10. Falcons 19,4 B posts
- 11. Seahawks 24,8 B posts
- 12. Broncos 31,4 B posts
- 13. WWIII 83,5 B posts
- 14. Steelers 124 B posts
- 15. Ravens 85,9 B posts
- 16. Paige 18,7 B posts
- 17. Kyle 45,9 B posts
- 18. Bears 118 B posts
- 19. 72 Dolphins N/A
- 20. #FTTB 4.659 posts
Who to follow
-
 Open Forum Infectious Diseases
Open Forum Infectious Diseases
@OFIDJournal -
 Clinical Infectious Diseases
Clinical Infectious Diseases
@CIDJournal -
 IDWeek
IDWeek
@IDWeekmtg -
 Journal of Infectious Diseases
Journal of Infectious Diseases
@JIDJournal -
 MAD-ID The Antimicrobial Stewardship Meeting®️
MAD-ID The Antimicrobial Stewardship Meeting®️
@MAD_ID_ASP -
 SHEA
SHEA
@SHEA_Epi -
 Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology
Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology
@ICHEJournal -
 transplantid.net
transplantid.net
@TransplantIDNet -
 IDBugBowl
IDBugBowl
@IdBowl -
 Infectious Diseases Community of Practice - AST
Infectious Diseases Community of Practice - AST
@AST_IDCOP -
 Stanford Antimicrobial Stewardship
Stanford Antimicrobial Stewardship
@StanfordASP -
 SIDP
SIDP
@SIDPharm -
 ACCP INFD PRN
ACCP INFD PRN
@accpinfdprn -
 Gonzalo Bearman
Gonzalo Bearman
@gonzalobearman -
 Women In Infectious Diseases (WIID)
Women In Infectious Diseases (WIID)
@Women_in_ID
Something went wrong.
Something went wrong.